
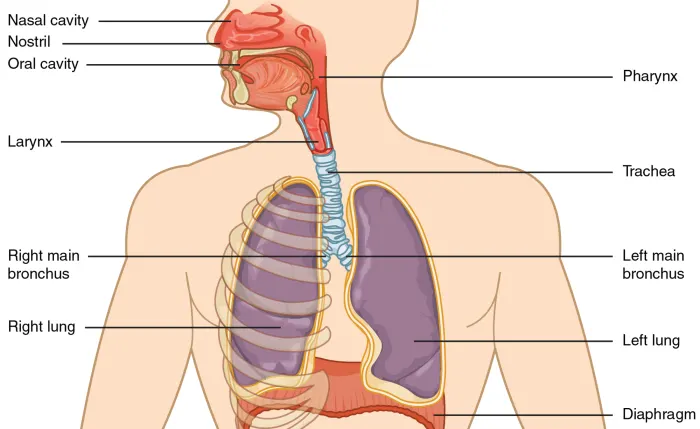
Respiratory system
| Word | Transcription | Part of Speech | English Explanation | Vietnamese Meaning | Notes (Examples or Related Words) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | /lʌŋz/ | Noun | The primary organs of respiration, responsible for gas exchange between the blood and the atmosphere. | Phổi | Example: The lungs are divided into lobes; the right lung has three, and the left has two. Related: pulmonary, lung capacity. |
| Trachea | /ˈtreɪkiə/ | Noun | The windpipe; a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi, allowing air passage to the lungs. | Khí quản | Example: The trachea is lined with cilia that filter particles from inhaled air. Related: tracheal, tracheotomy. |
| Bronchi | /ˈbrɒŋkaɪ/ | Noun | The two main air passages that branch from the trachea into the lungs. | Phế quản | Example: The bronchi further divide into smaller bronchioles. Related: bronchial, bronchitis. |
| Bronchioles | /ˈbrɒŋkiəʊlz/ | Noun | The smaller branches of the bronchi that lead to the alveoli in the lungs. | Tiểu phế quản | Example: Bronchioles are involved in the regulation of airflow to the alveoli. Related: bronchiolitis, bronchoconstriction. |
| Alveoli | /ælˈviːəlaɪ/ | Noun | Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs between the air and the blood. | Phế nang | Example: Oxygen diffuses into the blood from the alveoli, and carbon dioxide diffuses out. Related: alveolar, alveolitis. |
| Diaphragm | /ˈdaɪəˌfræm/ | Noun | A dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs, playing a major role in breathing by contracting and relaxing. | Cơ hoành | Example: The diaphragm contracts during inhalation, creating a vacuum that pulls air into the lungs. Related: diaphragmatic, diaphragm paralysis. |
| Larynx | /ˈlærɪŋks/ | Noun | The voice box; an organ involved in breathing, producing sound, and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. | Thanh quản | Example: The larynx contains the vocal cords. Related: laryngeal, laryngitis. |
| Pharynx | /ˈfærɪŋks/ | Noun | The throat; a muscular tube that connects the mouth and nasal passages to the esophagus and larynx. | Hầu | Example: The pharynx is involved in both respiration and digestion. Related: pharyngeal, pharyngitis. |
| Nasal Cavity | /ˈneɪzəl ˈkævɪti/ | Noun | The large air-filled space above and behind the nose that warms, moistens, and filters incoming air. | Khoang mũi | Example: The nasal cavity is lined with mucous membranes. Related: nasal septum, nasal passages. |
| Pleura | /ˈplʊərə/ | Noun | A double-layered membrane surrounding each lung, providing lubrication and reducing friction during breathing. | Màng phổi | Example: The pleura produces pleural fluid to facilitate lung movement. Related: pleuritis, pleural cavity. |
| Respiratory Rate | /rɪˈspɪrətɔːri reɪt/ | Noun | The number of breaths taken per minute, an important vital sign indicating respiratory function. | Tần số hô hấp | Example: The normal respiratory rate for adults is 12-20 breaths per minute. Related: tachypnea, bradypnea. |
| Tidal Volume | /ˈtaɪdəl ˈvɒljʊm/ | Noun | The amount of air inhaled or exhaled during a normal breath. | Thể tích khí lưu thông | Example: Tidal volume increases during exercise to meet oxygen demands. Related: lung capacity, spirometry. |
| Vital Capacity | /ˈvaɪtl kəˈpæsɪti/ | Noun | The maximum amount of air a person can exhale after maximum inhalation, an important measure of lung function. | Dung tích sống | Example: Vital capacity is reduced in restrictive lung diseases. Related: forced vital capacity, spirometry. |
| Spirometry | /spaɪˈrɒmɪtri/ | Noun | A common test used to assess lung function by measuring the volume of air inhaled and exhaled. | Phép đo phế dung | Example: Spirometry is used to diagnose conditions like asthma and COPD. Related: spirometer, pulmonary function test. |
| Oxygen Saturation | /ˈɒksɪdʒən ˌsætʃʊˈreɪʃən/ | Noun | The percentage of hemoglobin that is bound to oxygen in the blood, an indicator of respiratory efficiency. | Độ bão hòa oxy | Example: Normal oxygen saturation levels are between 95-100%. Related: pulse oximetry, hypoxemia. |
| Hypoxia | /haɪˈpɒksiə/ | Noun | A condition in which there is insufficient oxygen reaching the tissues, leading to impaired function. | Thiếu oxy | Example: Hypoxia can occur due to respiratory disorders, altitude, or cardiovascular issues. Related: hypoxic, anoxia. |
| Hypercapnia | /ˌhaɪpərˈkæpniə/ | Noun | A condition characterized by elevated levels of carbon dioxide in the blood, often due to inadequate respiration. | Tăng CO2 máu | Example: Hypercapnia can result from hypoventilation or lung disease. Related: respiratory acidosis, hypoventilation. |
| Pulmonary Edema | /ˈpʌlmənɛri ɪˈdiːmə/ | Noun | A condition characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lungs, making breathing difficult. | Phù phổi | Example: Pulmonary edema is a common complication of heart failure. Related: fluid overload, respiratory distress. |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) | /ˈkrɒnɪk əbˈstrʌktɪv ˈpʌlmənɛri dɪˈziːz/ | Noun | A group of progressive lung diseases, including emphysema and chronic bronchitis, that cause breathing difficulties. | Bệnh phổi tắc nghẽn mạn tính (COPD) | Example: COPD is primarily caused by smoking and long-term exposure to harmful pollutants. Related: emphysema, chronic bronchitis, airflow obstruction. |
| Asthma | /ˈæzmə/ | Noun | A chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, and coughing. | Hen suyễn | Example: Asthma triggers include allergens, exercise, and cold air. Related: bronchospasm, asthma attack. |
| Pneumonia | /njuːˈməʊniə/ | Noun | An infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, which may fill with fluid or pus, leading to difficulty breathing. | Viêm phổi | Example: Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Related: bacterial pneumonia, viral pneumonia, chest X-ray. |
| Tuberculosis | /tjuːˌbɜːrkjʊˈloʊsɪs/ | Noun | A serious infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, affecting mainly the lungs but can spread to other organs. | Bệnh lao | Example: Tuberculosis is spread through the air when a person with the active disease coughs or sneezes. Related: TB test, pulmonary tuberculosis. |
| Pleural Effusion | /ˈplʊərəl ɪˈfjuːʒən/ | Noun | The abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space, which can impair breathing by limiting lung expansion. | Tràn dịch màng phổi | Example: Pleural effusion can be caused by heart failure, infection, or cancer. Related: thoracentesis, pleurisy. |
| Pulmonary Embolism | /ˈpʌlmənɛri ˈɛmbəlɪzəm/ | Noun | A blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs, usually due to blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs. |
Respiratory system
