
Skin and Senses
| Skin | /skɪn/ | Noun | The largest organ of the body that covers and protects the underlying tissues and organs. | Da | Example: The skin acts as a barrier against pathogens. Related: epidermis, dermis, hypodermis. |
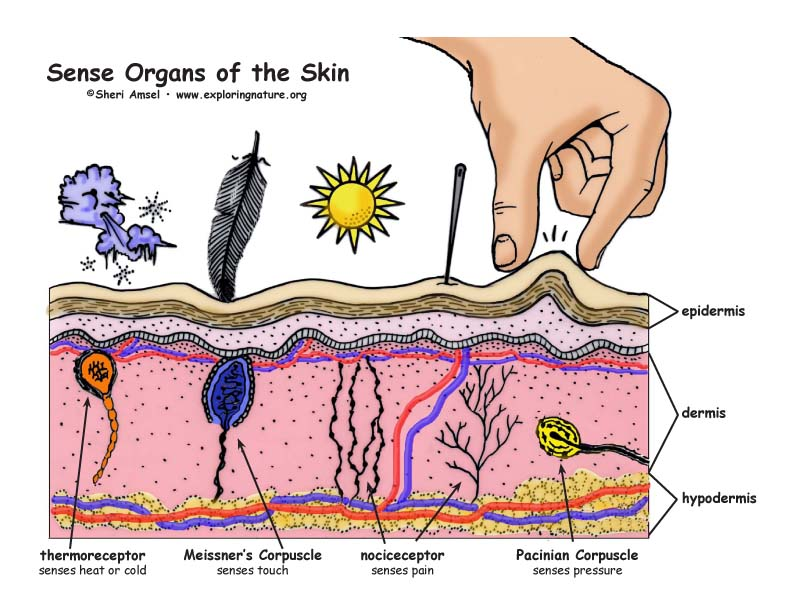
| Epidermis | /ˌɛpɪˈdɜːrmɪs/ | Noun | The outermost layer of the skin, which provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. | Biểu bì | Example: The epidermis contains keratinocytes, melanocytes, and Langerhans cells. Related: stratified squamous epithelium. |
| Dermis | /ˈdɜːrmɪs/ | Noun | The layer of skin between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, containing connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. | Trung bì | Example: The dermis provides structural support and elasticity to the skin. Related: collagen, elastin. |
| Hypodermis | /ˌhaɪpəʊˈdɜːrmɪs/ | Noun | The deepest layer of the skin, also known as the subcutaneous layer, which consists of loose connective tissue and fat. | Hạ bì | Example: The hypodermis insulates the body and absorbs shock. Related: subcutaneous tissue, adipose tissue. |
| Melanin | /ˈmɛlənɪn/ | Noun | A pigment responsible for the color of the skin, hair, and eyes, and protects against UV radiation. | Melanin | Example: Melanin production increases with sun exposure. Related: pigmentation, UV protection. |
| Keratin | /ˈkɛrətɪn/ | Noun | A protein found in the skin, hair, and nails that provides strength and protection. | Keratin | Example: Keratin helps form the protective outer layer of skin. Related: keratinocyte, alpha-keratin. |
| Sweat Gland | /swɛt ɡlænd/ | Noun | Glands in the skin that secrete sweat to regulate body temperature and remove waste products. | Tuyến mồ hôi | Example: Sweat glands are located in the dermis. Related: eccrine gland, apocrine gland. |
| Sebaceous Gland | /sɪˈbeɪʃəs ɡlænd/ | Noun | Glands in the skin that secrete sebum (oil) to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair. | Tuyến bã nhờn | Example: Sebaceous glands are often associated with hair follicles. Related: sebum, acne. |
| Retina | /ˈrɛtɪnə/ | Noun | The light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that converts light into neural signals. | Võng mạc | Example: The retina contains photoreceptor cells such as rods and cones. Related: visual perception, macula. |
| Cornea | /ˈkɔːrniə/ | Noun | The transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber, and helps focus light. | Giác mạc | Example: The cornea refracts light entering the eye. Related: refraction, lens. |
| Iris | /ˈaɪrɪs/ | Noun | The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil and regulates the amount of light entering the eye. | Mống mắt | Example: The iris adjusts the pupil size in response to light levels. Related: pupil, anterior chamber. |
| Pupil | /ˈpjuːpl/ | Noun | The opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the retina. | Con ngươi | Example: The pupil constricts in bright light and dilates in dim light. Related: light reflex, accommodation. |
| Lens | /lɛnz/ | Noun | The transparent structure inside the eye that focuses light onto the retina. | Thủy tinh thể | Example: The lens changes shape to focus on objects at varying distances. Related: accommodation, visual acuity. |
| Optic Nerve | /ˈɒptɪk nɜːrv/ | Noun | The nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. | Dây thần kinh thị giác | Example: The optic nerve is crucial for vision. Related: visual pathway, optic chiasm. |
| Cochlea | /ˈkɒkliə/ | Noun | A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled inner ear structure that helps convert sound vibrations into neural signals. | Ốc tai | Example: The cochlea contains hair cells that detect sound vibrations. Related: auditory system, inner ear. |
| Eardrum | /ˈɪərdrʌm/ | Noun | A thin membrane in the ear that vibrates in response to sound waves and transmits these vibrations to the middle ear bones. | Màng nhĩ | Example: The eardrum separates the outer ear from the middle ear. Related: tympanic membrane, hearing. |
| Vestibular System | /ˈvɛstɪˌbjuːlər ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The system responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation, located in the inner ear. | Hệ tiền đình | Example: The vestibular system works with the visual system to maintain balance. Related: equilibrium, proprioception. |
| Olfactory System | /ɒlˈfæktəri ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The sensory system responsible for the sense of smell. | Hệ khứu giác | Example: The olfactory system detects and processes odors. Related: olfaction, olfactory receptors. |
| Gustatory System | /ˈɡʌstəˌtɔːri ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The sensory system responsible for the sense of taste. | Hệ vị giác | Example: The gustatory system helps perceive different tastes through taste buds. Related: taste buds, papillae. |
| Taste Bud | /teɪst bʌd/ | Noun | Sensory organs on the tongue that detect taste and send information to the brain. | Nụ vị giác | Example: Taste buds can distinguish between sweet, salty, sour, and bitter tastes. Related: gustatory receptors. |
Skin and Senses
