
Reproductive system
| Reproductive System | /rɪˈprɒdʌktɪv ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The system of organs and structures involved in producing offspring and maintaining sexual function. | Hệ sinh sản | Example: The reproductive system includes the genital organs and related structures. Related: fertility, reproduction. |
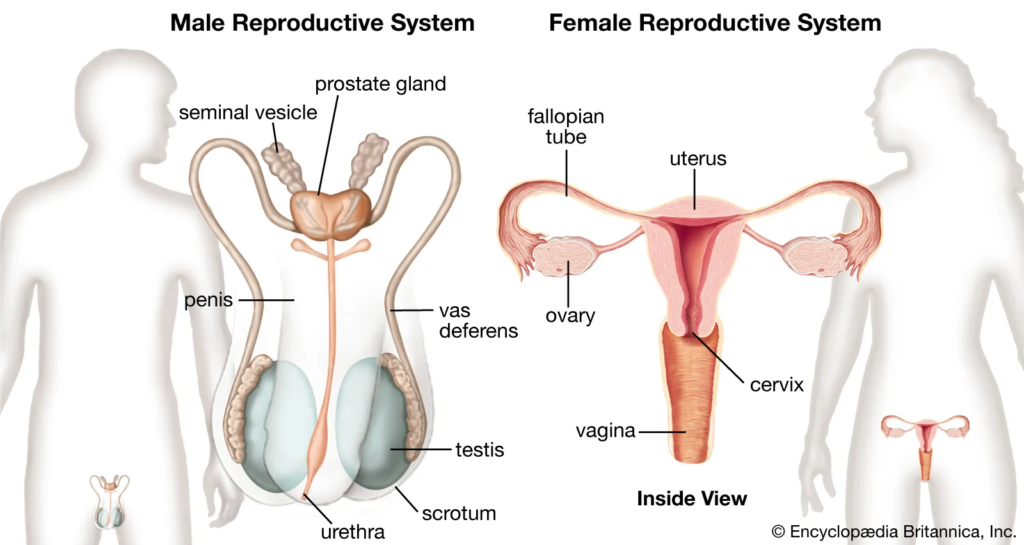
| Ovary | /ˈoʊvəri/ | Noun | The female reproductive organ that produces eggs (ova) and hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. | Buồng trứng | Example: The ovaries release eggs during ovulation. Related: follicle, corpus luteum. |
| Ovum (Ova) | /ˈoʊvəm/ | Noun | The female gamete or egg cell, which can be fertilized by sperm to form a zygote. | Trứng | Example: An ovum is released from the ovary during each menstrual cycle. Related: fertilization, oocyte. |
| Fallopian Tube | /fəˈloʊpiən tjuːb/ | Noun | A pair of tubes through which eggs travel from the ovaries to the uterus; also the site of fertilization. | Ống dẫn trứng | Example: The fallopian tubes transport the egg to the uterus. Related: fimbriae, ectopic pregnancy. |
| Uterus | /ˈjuːtərəs/ | Noun | The hollow, muscular organ in the female pelvis where a fertilized egg implants and develops during pregnancy. | Tử cung | Example: The uterus expands to accommodate the growing fetus during pregnancy. Related: endometrium, myometrium. |
| Endometrium | /ˌɛndəˈmiːtriəm/ | Noun | The inner lining of the uterus that thickens during the menstrual cycle and sheds if pregnancy does not occur. | Niêm mạc tử cung | Example: The endometrium provides a suitable environment for implantation. Related: menstrual cycle, implantation. |
| Myometrium | /ˌmaɪoʊˈmiːtriəm/ | Noun | The middle layer of the uterine wall, composed of smooth muscle tissue that contracts during labor. | Cơ tử cung | Example: The myometrium helps in expelling the fetus during childbirth. Related: labor contractions, uterine muscle. |
| Cervix | /ˈsɜːrvɪks/ | Noun | The lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina and serves as the birth canal during delivery. | Cổ tử cung | Example: The cervix dilates during labor to allow the passage of the baby. Related: cervical mucus, cervical canal. |
| Vagina | /vəˈdʒaɪnə/ | Noun | The muscular tube that connects the external genitals to the uterus and serves as the birth canal. | Âm đạo | Example: The vagina accommodates the penis during intercourse and serves as the passage for childbirth. Related: vaginal canal, vaginal discharge. |
| Penis | /ˈpiːnɪs/ | Noun | The male reproductive organ that delivers sperm into the female reproductive tract and functions as an organ for urination. | Dương vật | Example: The penis is involved in both sexual intercourse and urination. Related: urethra, erectile tissue. |
| Testis | /ˈtɛstɪs/ | Noun | The male reproductive organ that produces sperm and hormones such as testosterone. | Tinh hoàn | Example: The testis is responsible for sperm production and hormone secretion. Related: seminiferous tubules, epididymis. |
| Spermatozoon (Sperm) | /ˌspɜːrmætəˈzoʊən/ | Noun | The male gamete or sperm cell, responsible for fertilizing the female egg. | Tinh trùng | Example: Spermatozoa travel through the female reproductive tract to reach and fertilize the ovum. Related: sperm count, spermatogenesis. |
| Epididymis | /ˌɛpɪˈdɪmɪs/ | Noun | The coiled tube located at the back of the testis where sperm mature and are stored. | Ống dẫn tinh | Example: The epididymis stores and matures sperm until ejaculation. Related: vas deferens, sperm maturation. |
| Vas Deferens | /væs ˈdɛfərəns/ | Noun | The tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct. | Ống dẫn tinh | Example: The vas deferens is part of the pathway for sperm during ejaculation. Related: seminal vesicle, ejaculatory duct. |
| Seminal Vesicle | /ˈsɛmɪnəl ˈvɛsɪkl/ | Noun | Glands that secrete a fluid that nourishes and helps transport sperm during ejaculation. | Túi tinh | Example: Seminal vesicles contribute to the seminal fluid that makes up most of the ejaculate. Related: prostate gland, seminal fluid. |
| Prostate Gland | /ˈprɒsteɪt ˌɡlænd/ | Noun | A gland that produces a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm, also plays a role in urine control. | Tuyến tiền liệt | Example: The prostate gland surrounds the urethra and contributes to semen. Related: prostatic fluid, benign prostatic hyperplasia. |
| Urethra | /jʊˈriːθrə/ | Noun | The duct through which urine and sperm are expelled from the body. | Niệu đạo | Example: The urethra serves as a passage for both urine and semen. Related: urinary tract, ejaculatory duct. |
| Hormone | /ˈhɔːrməʊn/ | Noun | Chemical substances produced by glands that regulate various functions in the body, including reproduction. | Hormone | Example: Hormones such as estrogen and testosterone regulate reproductive functions. Related: endocrine system, hormonal cycle. |
| Estrogen | /ˈɛstroʊdʒən/ | Noun | A group of hormones responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system. | Estrogen | Example: Estrogen regulates the menstrual cycle and supports pregnancy. Related: progesterone, menstrual cycle. |
| Progesterone | /prəˈɡɛstərəʊn/ | Noun | A hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains it if fertilization occurs. | Progesterone | Example: Progesterone levels rise after ovulation to support implantation. Related: estrogen, luteal phase. |
| Testosterone | /tɛsˈtɒstərəʊn/ | Noun | The primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male reproductive tissues and characteristics. | Testosterone | Example: Testosterone regulates sperm production and secondary sexual characteristics. Related: androgen, puberty. |
| Fertilization | /ˌfɜːrtəlaɪˈzeɪʃən/ | Noun | The process of sperm merging with an ovum to form a zygote, leading to pregnancy. | Thụ tinh | Example: Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tube. Related: zygote, conception. |
| Menstruation | /ˌmɛnstrueɪˈʃən/ | Noun | The monthly shedding of the uterine lining through the vagina, also known as the menstrual period. | Kinh nguyệt | Example: Menstruation is a normal part of the female reproductive cycle. Related: menstrual cycle, menstruation symptoms. |
| Ovulation | /ˌoʊvjʊˈleɪʃən/ | Noun | The release of an ovum from the ovary, typically occurring mid-cycle. | Rụng trứng | Example: Ovulation is the key event for conception to occur. Related: luteal phase, follicular phase. |
| Pregnancy | /ˈprɛɡnənsi/ | Noun | The period during which a fertilized egg develops into a fetus and is carried in the uterus. | Mang thai | Example: Pregnancy lasts about 40 weeks and involves the development of the embryo and fetus. Related: gestation, prenatal care. |
| Parturition | /ˌpɑːrtjʊˈrɪʃən/ | Noun | The process of childbirth or labor, during which the fetus is delivered from the uterus. | Sinh đẻ | Example: Parturition involves labor stages and delivery of the baby. Related: labor, delivery, childbirth. |
Reproductive system
