
Immune system
| Immune System | /ɪˈmjun ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against harmful invaders. | Hệ miễn dịch | Example: The immune system protects the body from infections and diseases. Related: immunity, defense mechanisms. |
| Immunity | /ɪˈmjunɪti/ | Noun | The ability of the body to resist or eliminate potentially harmful pathogens or foreign substances. | Miễn dịch | Example: Immunity can be acquired through vaccination or exposure to pathogens. Related: innate immunity, adaptive immunity. |
| Antigen | /ˈæntɪdʒən/ | Noun | A substance that induces an immune response, typically a foreign protein or polysaccharide. | Kháng nguyên | Example: Pathogens have antigens that trigger an immune response. Related: antibody, immune response. |
| Antibody | /ˈæntɪbɒdi/ | Noun | A protein produced by the immune system in response to an antigen, which neutralizes or destroys the antigen. | Kháng thể | Example: Antibodies bind to antigens to help eliminate them from the body. Related: immunoglobulin, antibody response. |
| White Blood Cell (WBC) | /waɪt blʌd sɛl/ | Noun | Cells in the blood that are part of the immune system and help defend the body against infections. | Bạch cầu | Example: White blood cells include lymphocytes and neutrophils. Related: leukocyte, immune cell. |
| Lymphocyte | /ˈlɪmfəsaɪt/ | Noun | A type of white blood cell involved in the adaptive immune response, including T cells and B cells. | Tế bào lympho | Example: Lymphocytes are crucial for recognizing and responding to specific pathogens. Related: T cells, B cells. |
| T Cell | /tiː sɛl/ | Noun | A type of lymphocyte that matures in the thymus and is involved in cell-mediated immunity. | Tế bào T | Example: T cells help recognize and destroy infected cells. Related: helper T cells, cytotoxic T cells. |
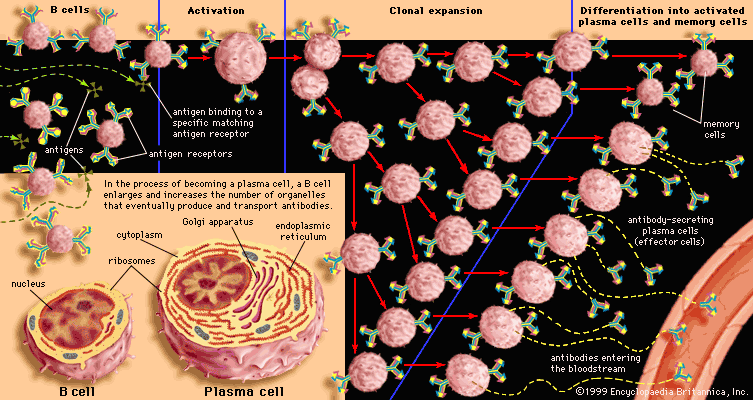
| B Cell | /biː sɛl/ | Noun | A type of lymphocyte that produces antibodies and matures in the bone marrow. | Tế bào B | Example: B cells are responsible for antibody-mediated immunity. Related: plasma cells, memory B cells. |
| Macrophage | /ˈmækrəfeɪdʒ/ | Noun | A type of white blood cell that engulfs and digests pathogens and dead cells through phagocytosis. | Đại thực bào | Example: Macrophages act as scavengers and help initiate the immune response. Related: phagocyte, antigen-presenting cell. |
| Dendritic Cell | /dɛnˈdrɪtɪk sɛl/ | Noun | A type of antigen-presenting cell that captures and presents antigens to T cells to initiate an immune response. | Tế bào hình gai | Example: Dendritic cells play a key role in bridging innate and adaptive immunity. Related: antigen-presenting cell. |
| Cytokine | /ˈsaɪtəˌkaɪn/ | Noun | Small proteins released by cells that affect the behavior of other cells and play a role in immune response regulation. | Cytokine | Example: Cytokines such as interleukins and interferons are involved in immune signaling. Related: immune signaling, inflammatory response. |
| Complement System | /ˈkɒmplɪˌmɛnt ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | A group of proteins in the blood that work with antibodies to destroy pathogens and promote inflammation. | Hệ thống bổ sung | Example: The complement system helps enhance the ability of antibodies and phagocytes to clear microbes. Related: complement cascade, opsonization. |
| Inflammation | /ˌɪnfləˈmeɪʃən/ | Noun | The body’s response to injury or infection, characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain. | Viêm | Example: Inflammation is a key component of the immune response and helps isolate and eliminate pathogens. Related: acute inflammation, chronic inflammation. |
| Phagocytosis | /ˌfæɡəʊsaɪˈtoʊsɪs/ | Noun | The process by which cells, such as macrophages, engulf and digest foreign particles or pathogens. | Sự thực bào | Example: Phagocytosis is crucial for removing pathogens and debris from the body. Related: phagocyte, engulfment. |
| Immunoglobulin (Ig) | /ˌɪmjunəʊˈɡlɒbjʊlɪn/ | Noun | A class of antibodies found in blood and other bodily fluids, essential for immune defense. | Globulin miễn dịch | Example: Immunoglobulins include IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD. Related: antibody, antibody-mediated immunity. |
| Vaccine | /ˈvæksiːn/ | Noun | A biological preparation that provides acquired immunity to a particular infectious disease. | Vắc-xin | Example: Vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight pathogens. Related: immunization, booster shot. |
| Autoimmune Disease | /ˌɔːtəʊɪˈmjun dɪˈziːz/ | Noun | A condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. | Bệnh tự miễn | Example: Examples of autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. Related: immune dysfunction, self-reactivity. |
Immune system
