| Endocrine System | /ˈɛndəʊkraɪn ˈsɪstəm/ | Noun | The system of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate various bodily functions. | Hệ nội tiết | Example: The endocrine system includes glands such as the thyroid, adrenal, and pituitary. Related: hormonal regulation, endocrine glands. |
| Hormone | /ˈhɔːrməʊn/ | Noun | Chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that regulate physiological processes. | Hormone | Example: Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Related: endocrine signaling, hormone receptor. |
| Pituitary Gland | /pɪˈtjuːɪtəri ɡlænd/ | Noun | A small gland at the base of the brain that controls other endocrine glands and produces hormones such as GH and ACTH. | Tuyến yên | Example: The pituitary gland is often referred to as the “master gland” because it regulates other endocrine glands. Related: growth hormone, ACTH. |
| Thyroid Gland | /ˈθaɪrɔɪd ɡlænd/ | Noun | A gland located in the neck that produces thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) which regulate metabolism. | Tuyến giáp | Example: Thyroid hormones regulate metabolic rate and growth. Related: hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism. |
| Parathyroid Glands | /ˌpærəˈθaɪrɔɪd ɡlændz/ | Noun | Glands located behind the thyroid that regulate calcium levels in the blood through parathyroid hormone (PTH). | Tuyến cận giáp | Example: The parathyroid glands secrete PTH to increase blood calcium levels. Related: calcium homeostasis, osteoclast. |
| Adrenal Glands | /əˈdriːnəl ɡlændz/ | Noun | Glands located on top of the kidneys that produce hormones such as cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenaline. | Tuyến thượng thận | Example: The adrenal glands release cortisol during stress. Related: adrenal cortex, adrenal medulla. |
| Cortisol | /ˈkɔːrtɪsɒl/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the adrenal cortex that helps the body respond to stress and regulates metabolism. | Cortisol | Example: Cortisol levels rise in response to stress. Related: glucocorticoids, stress response. |
| Aldosterone | /ælˈdɒstəroʊn/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the adrenal cortex that helps regulate blood pressure and electrolyte balance. | Aldosterone | Example: Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption in the kidneys. Related: sodium balance, blood pressure regulation. |
| Adrenaline (Epinephrine) | /ædˈrɛnəlɪn/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the adrenal medulla that prepares the body for ‘fight or flight’ responses. | Adrenaline (Epinephrine) | Example: Adrenaline increases heart rate and energy supply during stress. Related: sympathetic nervous system, catecholamines. |
| Insulin | /ˈɪnsəlɪn/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood glucose levels by facilitating cellular glucose uptake. | Insulin | Example: Insulin helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream. Related: diabetes, glucose metabolism. |
| Glucagon | /ˈɡluːkəɡən/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the pancreas that increases blood glucose levels by promoting glycogen breakdown. | Glucagon | Example: Glucagon stimulates the liver to release glucose into the blood. Related: glycogenolysis, glucose homeostasis. |
| Estrogen | /ˈɛstroʊdʒən/ | Noun | A group of hormones that regulate the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. | Estrogen | Example: Estrogen is involved in regulating the menstrual cycle. Related: progesterone, ovarian hormones. |
| Progesterone | /prəˈɡɛstərəʊn/ | Noun | A hormone that prepares the uterus for pregnancy and maintains it if fertilization occurs. | Progesterone | Example: Progesterone helps maintain the uterine lining during pregnancy. Related: estrogen, luteal phase. |
| Testosterone | /tɛsˈtɒstərəʊn/ | Noun | The primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male reproductive tissues and characteristics. | Testosterone | Example: Testosterone regulates sperm production and secondary sexual characteristics. Related: androgen, puberty. |
| Melatonin | /ˌmɛləˈtoʊnɪn/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the pineal gland that regulates sleep-wake cycles. | Melatonin | Example: Melatonin levels increase in response to darkness, promoting sleep. Related: circadian rhythm, sleep regulation. |
| Pineal Gland | /ˈpɪniəl ɡlænd/ | Noun | A small endocrine gland in the brain that produces melatonin, which influences sleep patterns. | Tuyến tùng | Example: The pineal gland helps regulate the body’s circadian rhythms. Related: melatonin, sleep-wake cycle. |
| Hypothalamus | /ˌhaɪpəˈθæləməs/ | Noun | A region of the brain that controls the pituitary gland and regulates various physiological processes including hunger, thirst, and temperature. | Hạ đồi | Example: The hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. Related: neuroendocrine function, homeostasis. |
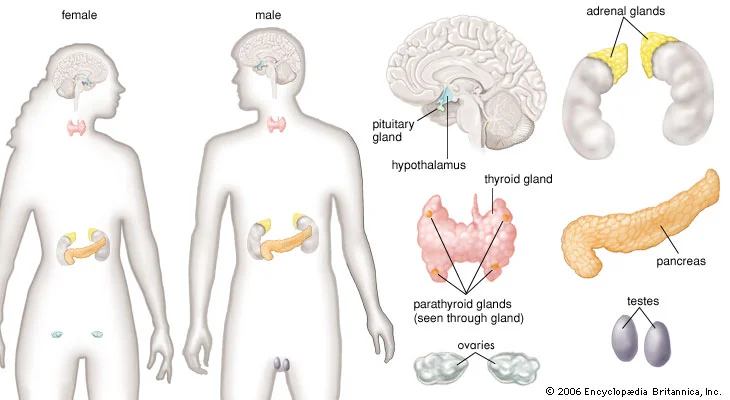
The endocrine system, a network of glands scattered throughout the body, is crucial for regulating long-term bodily functions via hormones. These chemical messengers interact with target cells to maintain homeostasis, promote growth, and coordinate various activities such as metabolism, immunity, and reproduction. Major glands include the pituitary (the “master” gland), thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries/testes, and others—each playing specialized roles. Hormones can act either as slow-acting yet impactful substances or faster neurotransmitters, influencing everything from energy balance to emotional responses. Growth hormone is one notable example that aids in physical development and tissue regeneration. Hormonal regulation is precise, ensuring specific cells respond without triggering uncoordinated actions.

