
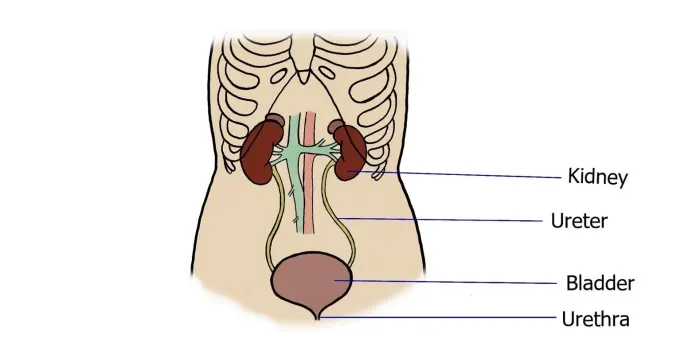
Urinary system
| Kidneys | /ˈkɪdniz/ | Noun | A pair of bean-shaped organs that filter blood to produce urine, removing waste and regulating fluid balance. | Thận | Example: The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining electrolyte balance. Related: renal, nephron, kidney stones. |
| Nephron | /ˈnɛfrɒn/ | Noun | The functional unit of the kidney, responsible for filtering blood and forming urine. | Đơn vị thận | Example: Each nephron consists of a glomerulus and a renal tubule. Related: glomerulus, renal corpuscle. |
| Glomerulus | /ɡlɒˈmɛrjʊləs/ | Noun | A network of capillaries in the nephron where blood filtration begins. | Cầu thận | Example: The glomerulus filters blood to form the glomerular filtrate. Related: Bowman’s capsule, glomerulonephritis. |
| Renal Tubule | /ˈriːnəl ˈtjuːbjuːl/ | Noun | The part of the nephron that processes the filtrate into urine by reabsorbing water and nutrients. | Ống thận | Example: The renal tubule is divided into the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal tubule. Related: tubular reabsorption, tubular secretion. |
| Ureter | /jʊˈriːtər/ | Noun | A tube that carries urine from each kidney to the bladder. | Niệu quản | Example: Ureters transport urine via peristaltic movements. Related: ureteral obstruction, ureteroscopy. |
| Bladder | /ˈblædər/ | Noun | A hollow organ that stores urine before it is excreted from the body. | Bàng quang | Example: The bladder can hold up to 500 mL of urine. Related: urinary bladder, cystitis, bladder capacity. |
| Urethra | /juːˈriːθrə/ | Noun | The tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination. | Niệu đạo | Example: The urethra is shorter in females than in males. Related: urethral sphincter, urethritis. |
| Urination | /ˌjʊərɪˈneɪʃən/ | Noun | The process of expelling urine from the bladder through the urethra. | Sự tiểu tiện | Example: Urination is controlled by the brain and spinal cord. Related: micturition, incontinence, urinary frequency. |
| Glomerular Filtration | /ɡlɒˈmɛrjʊlər fɪlˈtreɪʃən/ | Noun | The process by which the kidneys filter blood, removing excess wastes and fluids to form urine. | Lọc cầu thận | Example: Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is an indicator of kidney function. Related: GFR, kidney function test. |
| Renal Cortex | /ˈriːnəl ˈkɔːrtɛks/ | Noun | The outer layer of the kidney, containing the glomeruli and convoluted tubules. | Vỏ thận | Example: The renal cortex plays a key role in filtering blood and forming urine. Related: renal medulla, cortical nephron. |
| Renal Medulla | /ˈriːnəl məˈdʌlə/ | Noun | The innermost part of the kidney, where urine concentration occurs. | Tủy thận | Example: The renal medulla contains the loop of Henle and collecting ducts. Related: medullary nephron, renal pyramids. |
| Loop of Henle | /luːp ɒv ˈhɛnli/ | Noun | A section of the nephron that creates a concentration gradient in the kidney, allowing for urine concentration. | Quai Henle | Example: The loop of Henle plays a crucial role in water and sodium reabsorption. Related: countercurrent multiplier, nephron loop. |
| Collecting Duct | /kəˈlɛktɪŋ dʌkt/ | Noun | The final part of the nephron that transports urine from the renal tubules to the renal pelvis. | Ống góp | Example: The collecting duct is involved in the regulation of water and electrolyte balance. Related: antidiuretic hormone (ADH), renal papilla. |
| Renal Pelvis | /ˈriːnəl ˈpɛlvɪs/ | Noun | The funnel-shaped structure in the kidney that collects urine from the collecting ducts and leads to the ureter. | Bể thận | Example: The renal pelvis is the first part of the ureter. Related: hydronephrosis, pyelonephritis. |
| Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) | /ˌæntaɪˌdaɪjʊˈrɛtɪk ˈhɔːrməʊn/ | Noun | A hormone that regulates water balance in the body by increasing water reabsorption in the kidneys. | Hormone chống bài niệu | Example: ADH is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland. Related: vasopressin, water reabsorption. |
| Aldosterone | /ælˈdɒstərəʊn/ | Noun | A hormone that promotes sodium retention and potassium excretion in the kidneys, regulating blood pressure. | Aldosterone | Example: Aldosterone is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Related: sodium reabsorption, hyperaldosteronism. |
| Erythropoietin | /ɪˌrɪθrəˈpɔɪɪtɪn/ | Noun | A hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production in the bone marrow. | Erythropoietin | Example: Erythropoietin is released in response to low oxygen levels in the blood. Related: erythropoiesis, anemia. |
| Renin | /ˈriːnɪn/ | Noun | An enzyme produced by the kidneys that plays a key role in the regulation of blood pressure. | Renin | Example: Renin is part of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS). Related: angiotensin, blood pressure regulation. |
| Creatinine | /kriˈætɪniːn/ | Noun | A waste product from the normal breakdown of muscle tissue, filtered by the kidneys and excreted in urine. | Creatinine | Example: Elevated creatinine levels can indicate impaired kidney function. Related: blood urea nitrogen (BUN), kidney function test. |
| Urea | /jʊˈriːə/ | Noun | A waste product formed in the liver from the breakdown of proteins, excreted in the urine by the kidneys. | Ure | Example: Urea is the main nitrogenous waste product in urine. Related: blood urea nitrogen (BUN), urea cycle. |
| Diuretics | /ˌdaɪjʊˈrɛtɪks/ | Noun | Medications that increase urine production by promoting the excretion of water and salts from the body. | Thuốc lợi tiểu | Example: Diuretics are commonly used to treat high blood pressure and edema. Related: loop diuretics, thiazide diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics. |
| Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) | /ˈjʊrɪnəri trækt ɪnˈfɛkʃən/ | Noun | An infection in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. | Nhiễm trùng đường tiểu | Example: UTIs are more common in women and can cause symptoms like pain during urination. Related: cystitis, pyelonephritis. |
| Pyelonephritis | /ˌpaɪələʊnɪˈfraɪtɪs/ | Noun | A type of urinary tract infection that reaches the kidney, causing inflammation and potentially serious damage. | Viêm thận bể thận | Example: Pyelonephritis can result from untreated bladder infections. Related: kidney infection, chronic pyeloneph |
Urinary system
