
Nervous system
| Neuron | /ˈnʊərɒn/ | Noun | A nerve cell that transmits electrical impulses in the brain and throughout the nervous system. | Tế bào thần kinh | Example: Neurons communicate with each other via synapses. Related: neuronal, neurotransmitter. |
| Synapse | /ˈsɪnæps/ | Noun | The junction between two nerve cells, where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals. | Khớp thần kinh | Example: The synapse allows neurons to pass electrical or chemical signals. Related: synaptic, synaptogenesis. |
| Axon | /ˈæksɒn/ | Noun | The long, slender projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron’s cell body. | Sợi trục thần kinh | Example: Axons can be covered with myelin to increase the speed of transmission. Related: axonal, axon terminal. |
| Dendrite | /ˈdɛndraɪt/ | Noun | The branched projections of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons. | Sợi nhánh | Example: Dendrites play a key role in the transmission of signals to the neuron’s cell body. Related: dendritic, dendritic spines. |
| Myelin | /ˈmaɪəlɪn/ | Noun | A fatty substance that surrounds the axon of some nerve cells, forming an insulating layer. | Myelin | Example: Myelin sheaths are essential for the fast transmission of nerve impulses. Related: myelination, myelin sheath. |
| Glial Cells | /ˈɡlaɪəl sɛlz/ | Noun | Non-neuronal cells in the nervous system that provide support and protection for neurons. | Tế bào thần kinh đệm | Example: Glial cells include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia. Related: neuroglia, glial function. |
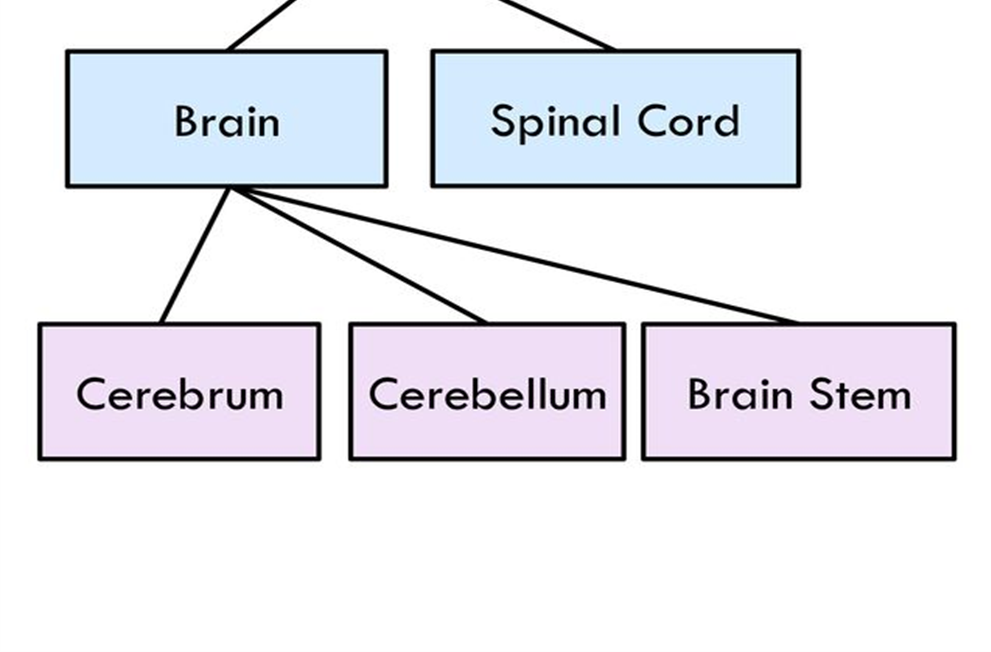
| Cerebrum | /səˈriːbrəm/ | Noun | The largest part of the brain, responsible for voluntary actions, speech, senses, thought, and memory. | Đại não | Example: The cerebrum is divided into two hemispheres. Related: cerebral cortex, cerebral hemispheres. |
| Cerebellum | /ˌsɛrəˈbɛləm/ | Noun | A region of the brain that coordinates voluntary movements such as posture, balance, and speech. | Tiểu não | Example: The cerebellum helps maintain balance and coordination. Related: cerebellar, cerebellar peduncles. |
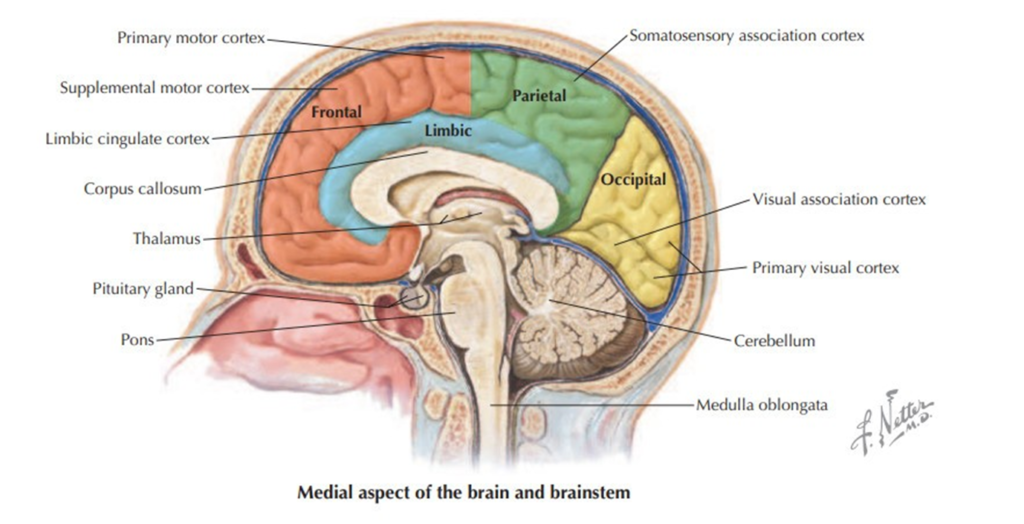
| Brainstem | /ˈbreɪnˌstɛm/ | Noun | The posterior part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord and controls vital functions. | Thân não | Example: The brainstem regulates heart rate, breathing, and sleep cycles. Related: medulla oblongata, pons, midbrain. |
| Spinal Cord | /ˈspaɪnəl kɔːd/ | Noun | The cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers that extends from the brainstem down the spinal column, transmitting signals. | Tủy sống | Example: The spinal cord acts as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body. Related: spinal nerves, central nervous system. |
| Peripheral Nerves | /pəˈrɪfərəl nɜːvz/ | Noun | Nerves located outside the brain and spinal cord, responsible for transmitting signals to and from the central nervous system. | Dây thần kinh ngoại vi | Example: Peripheral nerves include sensory and motor nerves. Related: peripheral neuropathy, peripheral nervous system. |
| Autonomic Nervous System | /ˌɔːtəˈnɒmɪk ˈnɜːvəs ˈsɪstɪm/ | Noun | The part of the nervous system that controls involuntary functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate. | Hệ thần kinh tự chủ | Example: The autonomic nervous system is divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Related: autonomic functions, autonomic dysreflexia. |
| Sympathetic Nervous System | /ˌsɪmpəˈθɛtɪk ˈnɜːvəs ˈsɪstɪm/ | Noun | A division of the autonomic nervous system that prepares the body for stressful or emergency situations. | Hệ thần kinh giao cảm | Example: The sympathetic nervous system triggers the “fight or flight” response. Related: sympathetic chain, sympathetic response. |
| Parasympathetic Nervous System | /ˌpærəˌsɪmpəˈθɛtɪk ˈnɜːvəs ˈsɪstɪm/ | Noun | A division of the autonomic nervous system that conserves energy and restores the body to a state of calm. | Hệ thần kinh phó giao cảm | Example: The parasympathetic nervous system promotes “rest and digest” activities. Related: parasympathetic tone, vagus nerve. |
| Thalamus | /ˈθæləməs/ | Noun | A brain structure that acts as a relay station, transmitting sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex. | Đồi thị | Example: The thalamus is involved in sensory perception and regulation of motor functions. Related: thalamic, thalamocortical. |
| Hypothalamus | /ˌhaɪpəˈθæləməs/ | Noun | A small region of the brain that controls many bodily functions, including temperature regulation, hunger, and hormone release. | Vùng hạ đồi | Example: The hypothalamus links the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Related: hypothalamic, hypothalamic-pituitary axis. |
| Amygdala | /əˈmɪɡdələ/ | Noun | A brain structure involved in processing emotions, particularly fear and pleasure. | Hạch hạnh nhân | Example: The amygdala plays a key role in the formation of emotional memories. Related: amygdaloid, limbic system. |
| Corpus Callosum | /ˌkɔːrpəs kəˈloʊsəm/ | Noun | A thick band of nerve fibers that connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres, enabling communication between them. | Thể chai | Example: The corpus callosum facilitates communication between the two sides of the brain. Related: interhemispheric, split-brain. |
| Meninges | /məˈnɪndʒiːz/ | Noun | The three protective membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. | Màng não | Example: The meninges consist of the dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater. Related: meningitis, meningeal. |
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | /səˌriːbroʊˈspaɪnəl ˈfluːɪd/ | Noun | A clear, colorless body fluid found in the brain and spinal cord that cushions the brain and removes waste. | Dịch não tủy | Example: Cerebrospinal fluid circulates through the ventricles of the brain. Related: CSF, lumbar puncture. |
| Blood-Brain Barrier | /ˌblʌdˈbreɪn ˈbæriər/ | Noun | A selective barrier that prevents certain substances from entering the brain while allowing others to pass. | Hàng rào máu não | Example: The blood-brain barrier protects the brain from harmful substances in the blood. Related: permeability, neuroprotection. |
Nervous system
