
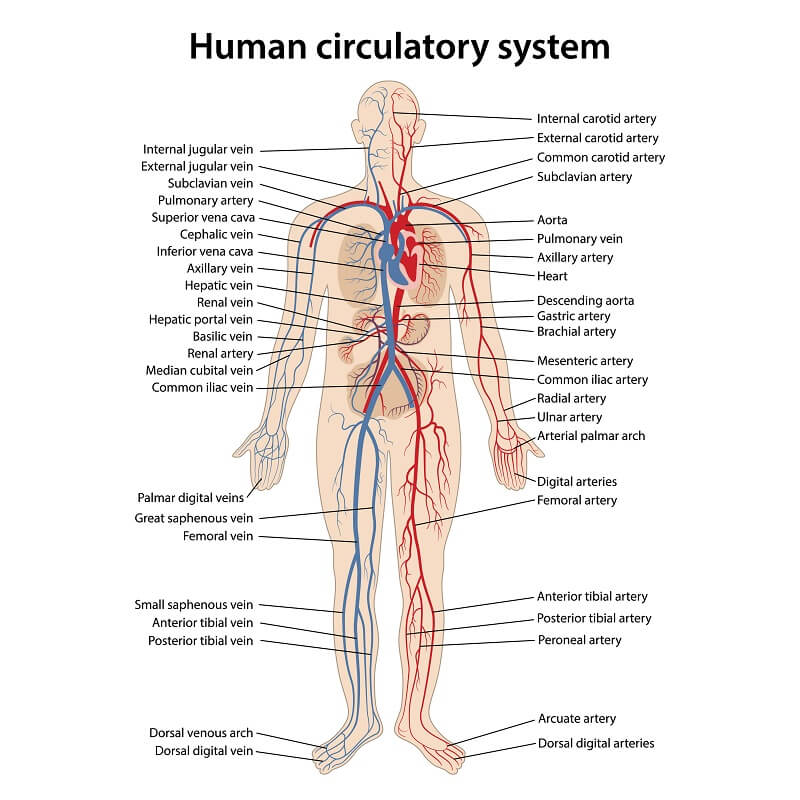
Circulatory system
| Heart | /hɑːrt/ | Noun | A muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system by rhythmic contractions. | Tim | Example: The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. Related: cardiac, cardiology. |
| Artery | /ˈɑːrtəri/ | Noun | A blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body tissues. | Động mạch | Example: The aorta is the largest artery in the body. Related: arterial, arteriogram. |
| Vein | /veɪn/ | Noun | A blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood towards the heart. | Tĩnh mạch | Example: The vena cava is a large vein that carries blood to the heart. Related: venous, phlebology. |
| Capillary | /kəˈpɪləri/ | Noun | The smallest blood vessels in the body, where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged with tissues. | Mao mạch | Example: Capillaries connect arterioles and venules. Related: capillary bed, microcirculation. |
| Aorta | /eɪˈɔːrtə/ | Noun | The largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart. | Động mạch chủ | Example: The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Related: aortic, aortic arch. |
| Ventricle | /ˈvɛntrɪkəl/ | Noun | One of the two lower chambers of the heart responsible for pumping blood out of the heart. | Tâm thất | Example: The left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to the body. Related: ventricular, ventricular fibrillation. |
| Atrium | /ˈeɪtriəm/ | Noun | One of the two upper chambers of the heart that receives blood returning to the heart. | Tâm nhĩ | Example: The right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the body. Related: atrial, atrial fibrillation. |
| Pulmonary Artery | /ˈpʌlmənɛri ˈɑːrtəri/ | Noun | The artery that carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs. | Động mạch phổi | Example: The pulmonary artery is unique as it carries deoxygenated blood. Related: pulmonary circulation, pulmonary embolism. |
| Pulmonary Vein | /ˈpʌlmənɛri veɪn/ | Noun | The vein that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart. | Tĩnh mạch phổi | Example: The pulmonary veins are the only veins that carry oxygenated blood. Related: pulmonary circulation, pulmonary hypertension. |
| Atrioventricular Valve | /ˌeɪtrioʊvɛnˈtrɪkjʊlər vælv/ | Noun | The valve located between the atrium and ventricle that prevents backflow of blood. | Van nhĩ thất | Example: The tricuspid valve is an atrioventricular valve on the right side of the heart. Related: mitral valve, bicuspid valve. |
| Semilunar Valve | /ˌsɛmɪˈluːnər vælv/ | Noun | The valve located at the exit of each ventricle, preventing backflow of blood into the heart. | Van bán nguyệt | Example: The aortic valve is a semilunar valve between the left ventricle and the aorta. Related: pulmonary valve, valvular. |
| Endocardium | /ˌɛndəʊˈkɑːrdiəm/ | Noun | The thin, smooth membrane lining the inside of the heart’s chambers. | Nội tâm mạc | Example: The endocardium is essential for preventing blood clot formation inside the heart. Related: endocarditis, endocardial. |
| Myocardium | /ˌmaɪəˈkɑːrdiəm/ | Noun | The thick muscular layer of the heart wall responsible for contracting and pumping blood. | Cơ tim | Example: The myocardium is thicker in the left ventricle than in the right. Related: myocardial infarction, myocarditis. |
| Pericardium | /ˌpɛrɪˈkɑːrdiəm/ | Noun | The double-walled sac containing the heart, providing protection and lubrication. | Ngoại tâm mạc | Example: The pericardium helps prevent the heart from overexpanding. Related: pericardial fluid, pericarditis. |
| Sinoatrial Node | /ˌsaɪnəʊˈeɪtriəl noʊd/ | Noun | The heart’s natural pacemaker that initiates each heartbeat. | Nút xoang nhĩ | Example: The sinoatrial node sets the rhythm of the heartbeat. Related: SA node, sinus rhythm. |
| Cardiac Cycle | /ˈkɑːrdiæk ˈsaɪkəl/ | Noun | The sequence of events in one heartbeat, including contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles. | Chu kỳ tim | Example: The cardiac cycle consists of systole and diastole phases. Related: systolic, diastolic. |
| Systole | /ˈsɪstəli/ | Noun | The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts and pumps blood. | Tâm thu | Example: During systole, the ventricles contract and push blood into the arteries. Related: systolic pressure, systolic function. |
| Diastole | /daɪˈæstəli/ | Noun | The phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle relaxes and fills with blood. | Tâm trương | Example: During diastole, the heart chambers fill with blood. Related: diastolic pressure, diastolic dysfunction. |
| Electrocardiogram | /ɪˌlɛktrəʊˈkɑːrdiəɡræm/ | Noun | A test that measures the electrical activity of the heart to detect abnormalities. | Điện tâm đồ | Example: An electrocardiogram is used to diagnose heart conditions. Related: ECG, EKG. |
| Hemoglobin | /ˈhiːməˌɡloʊbɪn/ | Noun | A protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. | Huyết sắc tố | Example: Hemoglobin binds oxygen in the lungs and releases it in tissues. Related: hemoglobinopathy, oxyhemoglobin. |
| Platelet | /ˈpleɪtlət/ | Noun | A small cell fragment in the blood that helps with clotting. | Tiểu cầu | Example: Platelets aggregate to form a blood clot. Related: thrombocyte, thrombopoiesis. |
| Plasma | /ˈplæzmə/ | Noun | The liquid component of blood in which the blood cells are suspended. | Huyết tương | Example: Plasma contains water, salts, and proteins. Related: plasma proteins, plasma exchange. |
| Blood Pressure | /ˈblʌd ˈprɛʃər/ | Noun | The force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels. | Huyết áp | Example: High blood pressure is known as hypertension. Related: systolic pressure, diastolic pressure. |
| Hypertension | /ˌhaɪpərˈtɛnʃən/ | Noun | A condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is consistently too high. | Tăng huyết áp | Example: Hypertension increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. Related: antihypertensive, primary hypertension. |
| Atherosclerosis | /ˌæθəroʊˌsklɛrəˈsɪs/ | Noun | A condition in which the arteries become narrowed and hardened due to plaque buildup. | Xơ vữa động mạch | Example: Atherosclerosis can lead to heart attacks and strokes. Related: atheroma, arterial plaque. |
Circulatory system
